Spring Cloud Auto-Config Java
11 Minute Read
Overview
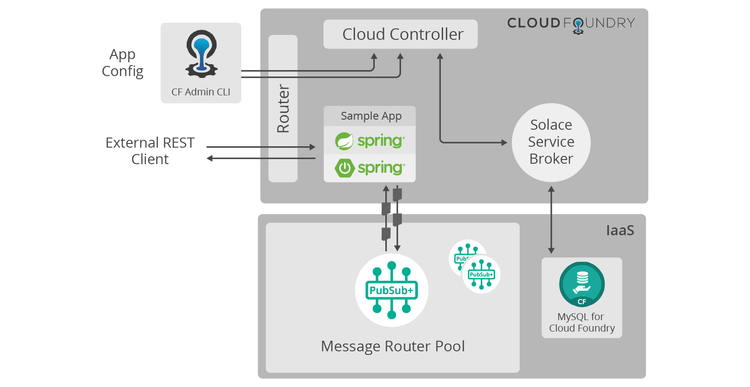
This tutorial is part of a series of tutorials which aims to introduce users to Solace PubSub+ in Pivotal Cloud Foundry. Solace PubSub+ in Pivotal Cloud Foundry is delivered as a Tile on the Pivotal Network. You can see the Solace PubSub+ for Pivotal Cloud Foundry Documentation for full details.
This tutorial is similar to the Spring Cloud tutorial. Like the Spring Cloud tutorial, it will introduce you to Solace PubSub+ for Pivotal Cloud Foundry by creating a Java application. In contrast to the Spring Cloud, this application uses solace-java-spring-boot which using the Java CFEnv library and Spring Auto Configuration can auto inject a SpringJCSMPFactory directly into your application.
Goals
The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate auto injecting a SpringJCSMPFactory based on the application's Cloud Foundry Service Bindings and connect to the Solace PubSub+ service instance. This tutorial will show you:
- How to Autowire a SpringJCSMPFactory into your application
- How to Autowire the SolaceServiceCredentials provided by the Cloud Foundry environment using Java CFEnv.
- How to Autowire SpringJCSMPFactoryCloudFactory which you can use to access other Cloud Available Solace PubSub+ Instances and create other instances of SpringJCSMPFactory.
- How to establish a connection to the Solace PubSub+ service.
- How to publish, subscribe and receive messages.
Assumptions
This tutorial assumes the following:
- You are familiar with Solace core concepts.
- You are familiar with Spring RESTful Web Services.
- You are familiar with Cloud Foundry.
- You have access to a running Pivotal Cloud Foundry environment.
- Solace PubSub+ for PCF has been installed in your Pivotal Cloud Foundry environment.
Obtaining the Solace API
This tutorial depends on you having the Solace PubSub+ API for Java (JCSMP). Here are a few easy ways to get the Java API. The instructions in the Building section assume you're using Gradle and pulling the jars from maven central. If your environment differs then adjust the build instructions appropriately.
Get the API: Using Gradle
compile("com.solacesystems:sol-jcsmp:10.+")Get the API: Using Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>com.solacesystems</groupId>
<artifactId>sol-jcsmp</artifactId>
<version>10.+</version>
</dependency>Get the API: Using the Solace Developer Portal
The Java API library can be downloaded here. The Java API is distributed as a zip file containing the required jars, API documentation, and examples.
Code Walk Through
This section will explain what the code in the samples does.
Structure
The sample application contains the following source files :
| Source File | Description |
|---|---|
| Application.java | The Sprint Boot application class |
| SolaceController.java | The Application's REST controller which provides an interface to subscribe, publish and receive messages. This class also implements the initialization procedure which connects the application to the Solace PubSub+ Service. |
| SimpleMessage.java | This class wraps the information to be stored in a message |
| SimpleSubscription.java | This class wraps the information describing a topic subscription |
This tutorial will only cover the source code in SolaceController.java and the necessary project dependencies as the other files do not contain logic related to establishing a connection to the Solace PubSub+ Service.
Obtaining the Solace Credentials in the Application
The Pivotal Cloud Foundry environment exposes any bound Service Instances in a JSON document stored in the VCAP_SERVICES environment variable. Here is an example of a VCAP_SERVICES with all the fields of interest to us:
{
"VCAP_SERVICES": {
"solace-pubsub": [ {
"name": "solace-pubsub-sample-instance",
"label": "solace-pubsub",
"plan": "enterprise-shared",
"tags": [
(...)
],
"credentials": {
"clientUsername": "v005.cu000001",
"clientPassword": "bb90fcb0-6c83-4a10-bafa-3ec225bbfc08",
"msgVpnName": "v005",
(...)
"smfHosts": [ "tcp://192.168.132.14:7000" ],
(...)
}
}
}
]
}You can see the full structure of the Solace PubSub+ VCAP_SERVICES in the Solace PubSub+ for PCF documentation.
This sample uses the solace-java-spring-boot which can auto detect and auto wire the available Solace PubSub+ Services from the Cloud Foundry environment into your application.
Spring provided @Autowire is used to access all auto configuration available beans which include an auto selected Factory.
// A JCSMP Factory for the auto selected Solace PubSub+ service,
// This is used to create JCSMPSession(s)
// This is the only required bean to run this application.
@Autowired
private SpringJCSMPFactory solaceFactory;
// The auto selected Solace PubSub+ service for the matching SpringJCSMPFactory,
// the relevant information provided by this bean have already been injected
// into the SpringJCSMPFactory
// This bean is for information only, it can be used to discover more about
// the solace service in use.
@Autowired
SolaceServiceCredentials solaceServiceCredentials;
// A Factory of Factories
// Has the ability to create SpringJCSMPFactory(s) for any available
// SolaceServiceCredentials
// Can be used in case there are multiple Solace PubSub+ Services to
// select from.
@Autowired
SpringJCSMPFactoryCloudFactory springJCSMPFactoryCloudFactory;The init() method retrieves and shows the autowired Solace PubSub+ Service Instance details as follows:
logger.info(String.format("SpringJCSMPFactoryCloudFactory discovered %s solace-pubsub service(s)",
springJCSMPFactoryCloudFactory.getSolaceServiceCredentials().size()));
// Log what Solace PubSub+ Services were discovered
for (SolaceServiceCredentials discoveredSolaceMessagingService : springJCSMPFactoryCloudFactory.getSolaceServiceCredentials()) {
logger.info(String.format("Discovered Solace PubSub+ service '%s': HighAvailability? ( %s ), Message VPN ( %s )",
discoveredSolaceMessagingService.getId(), discoveredSolaceMessagingService.isHA(),
discoveredSolaceMessagingService.getMsgVpnName()));
}Connecting to the Solace PubSub+ Service
The SpringJCSMPFactory solaceFactory was already autowired, you can use it to connect the Solace Session in the conventional way as outlined in the Publish/Subscribe tutorial. Use the solaceFactory to create a Session:
try {
logger.info(String.format("Creating a Session using a SolaceFactory configured with solace-pubsub service '%s'", solaceServiceCredentials.getId()));
session = solaceFactory.createSession();
session.connect();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error connecting and setting up session.", e);
logger.info("************* Aborting Solace initialization!! ************");
return;
}With the Solace session connected and aside from Providing other Properties to the application section, the remainder of this tutorial is the same as the Spring Cloud tutorial. The details are repeated here for convenience.
Creating the Message Consumer and Producer
To receive and send messages you will need to create a consumer and a producer by using the connected session. The following code will create a simple message producer that is silent normally but will log any errors it receives:
private class SimplePublisherEventHandler implements JCSMPStreamingPublishEventHandler {
@Override
public void responseReceived(String messageID) {
logger.info("Producer received response for msg: " + messageID);
}
@Override
public void handleError(String messageID, JCSMPException e, long timestamp) {
logger.error("Producer received error for msg: " + messageID + " - " + timestamp, e);
}
};
producer = session.getMessageProducer(new SimplePublisherEventHandler());The following code will create a simple message consumer that will log any incoming messages and errors:
private class SimpleMessageListener implements XMLMessageListener {
@Override
public void onReceive(BytesXMLMessage receivedMessage) {
numMessagesReceived.incrementAndGet();
if (receivedMessage instanceof TextMessage) {
lastReceivedMessage = (TextMessage) receivedMessage;
logger.info("Received message : " + lastReceivedMessage.getText());
} else {
logger.error("Received message that was not a TextMessage: " + receivedMessage.dump());
}
}
@Override
public void onException(JCSMPException e) {
logger.error("Consumer received exception: %s%n", e);
}
};
final XMLMessageConsumer cons = session.getMessageConsumer(new SimpleMessageListener());
cons.start();Publishing, Subscribing and Receiving Messages
The consumer created in the previous step will only receive messages matching topics that the Solace session subscribed to. It is thus necessary to create subscriptions in order to receive messages. You can add a topic subscription by sending a POST to the /subscription REST endpoint. The payload of the POST is a simple JSON structure containing the topic subscripion. For example: {"subscription": "test"}. Here is the method signature:
@RequestMapping(value = "/subscription", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<String> addSubscription(@RequestBody SimpleSubscription subscription) {
// ...
}You can send a message by sending a POST to the /message REST endpoint. The payload of the POST is a simple JSON structure containing the topic for publishing and the message contents. For example: {"topic": "test", "body": "Test Message"}. Here is the method signature:
@RequestMapping(value = "/message", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<String> sendMessage(@RequestBody SimpleMessage message) {
// ...
}Receiving messages is done at the backend via the SimpleMessageListener listener described above. This sample stores the last message received. To access ths received message you can send a GET request to /message endpoint. The same JSON structure of a message will be returned in the payload of the GET.
@RequestMapping(value = "/message", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<SimpleMessage> getLastMessageReceived() {
// ...
}The subscription JSON document used by the /subscription endpoint is modeled by the SimpleSubscription class, whereas the /message endpoint JSON document is modeled by the SimpleMessage class.
For more details on sending and receiving messages, you can checkout the JCSMP Publish/Subscribe tutorial.
Building
The full source code for this example is available in GitHub. To build, just clone and use gradle. Here is an example:
git clone https://github.com/SolaceSamples/solace-samples-cloudfoundry-java
cd solace-samples-cloudfoundry-java
./gradlew buildCloud Foundry Setup
The sample application specifies a dependency on a service instance named solace-pubsub-sample-instance in its manifiest (See spring-cloud-autoconf/manifest.yml). This must be an instance of the Solace PubSub+ Service which can be created with this command:
cf create-service solace-pubsub enterprise-shared solace-pubsub-sample-instanceDeploying
To deploy this tutorial's application you first need to go inside it's project directory and then push the application:
cd spring-cloud-autoconf-java
cf pushThis will push the application and will give the application the name specified by the manifest: solace-sample-spring-cloud-autoconf-java.
Providing other Properties to the application.
The configuration properties affecting the creation of Sessions is stored in SolaceJavaProperties, the Auto Configuration takes care of injecting Cloud Provided Solace PubSub+ Credentials into the SolaceJavaProperties which is used by the SpringJCSMPFactory instance.
Additional properties can be set in SolaceJavaProperties, for naming details refer to the Application Properties section of solace-java-spring-boot. Example of setting reconnectRetryWaitInMillis to 5000 milliseconds, and reapplySubscriptions to 'true':
cd spring-cloud-autoconf
cf set-env solace-sample-spring-cloud-autoconf solace.java.SOLACE_JAVA_RECONNECT_RETRY_WAIT_IN_MILLIS 5000
cf set-env solace-sample-spring-cloud-autoconf solace.java.SOLACE_JAVA_REAPPLY_SUBSCRIPTIONS true
cf restage solace-sample-spring-cloud-autoconfTrying Out The Application
As described above, the sample application has a simple REST interface that allows you to:
- Subscribe to a topic
- Send a message to a topic
- Receive a message
- Unsubscribe from a topic
In order to interact with the application you need to determine the application's URL. These shell commands can be used to quickly find out the URL:
export APP_NAME=solace-sample-spring-cloud-autoconf
export APP_URL=`cf apps | grep $APP_NAME | grep started | awk '{ print $6}'`
echo "The application URL is: ${APP_URL}"To demonstrate the application we will make the application send a message to itself. Then we will read the message back to confirm the successful delivery of the message :
# Subscribes the application to the topic "test"
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8" -d '{"subscription": "test"}' http://$APP_URL/subscription
# Send message with topic "test" and this content: "TEST_MESSAGE"
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8" -d '{"topic": "test", "body": "Test Message"}' http://$APP_URL/message
# The message should have been asynchronously received by the application. Check that the message was indeed received:
curl -X GET http://$APP_URL/message
# Unsubscribe the application from the topic "test"
curl -X DELETE http://$APP_URL/subscription/test