Publish/Subscribe
8 Minute Read
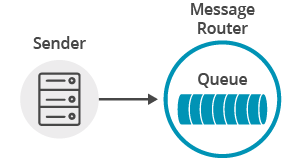
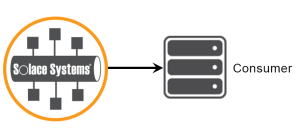
This tutorial will show you to how to connect a Apache Qpid JMS 2.0 API client to Solace Messaging using AMQP, add a topic subscription and publish a message matching this topic subscription. This is the publish/subscribe message exchange pattern as illustrated here:
At the end, this tutorial walks through downloading and running the sample from source.
This tutorial focuses on using a non-Solace JMS API implementation. For using the Solace JMS API see Solace Getting Started JMS Tutorials.
Assumptions
This tutorial assumes the following:
- You are familiar with Solace core concepts.
-
You have access to Solace messaging with the following configuration details:
- Connectivity information for a Solace message-VPN
- Enabled client username and password
One simple way to get access to Solace messaging quickly is to create a messaging service in Solace Cloud as outlined here. You can find other ways to get access to Solace messaging below.
Goals
The goal of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to use Apache Qpid JMS 2.0 API over AMQP using Solace messaging. This tutorial will show you:
- How to build and send a message on a topic
- How to subscribe to a topic and receive a message
Get Solace Messaging
This tutorial requires access Solace PubSub+ messaging and requires that you know several connectivity properties about your Solace messaging. Specifically you need to know the following:
| Resources | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Host | String | This is the address clients use when connecting to the PubSub+ messaging to send and receive messages. (Format: DNS_NAME:Port or IP:Port) |
| Message VPN | String | The PubSub+ message router Message VPN that this client should connect to. |
| Client Username | String | The client username. (See Notes below) |
| Client Password | String | The client password. (See Notes below) |
There are several ways you can get access to PubSub+ Messaging and find these required properties.
Option 1: Use PubSub+ Cloud
- Follow these instructions to quickly spin up a cloud-based PubSub+ messaging service for your applications.
-
The messaging connectivity information is found in the service details in the connectivity tab (shown below). You will need:
- Host:Port (use the SMF URI)
- Message VPN
- Client Username
- Client Password

Option 2: Start a PubSub+ Software
-
Follow these instructions to start the PubSub+ Software in leading Clouds, Container Platforms or Hypervisors. The tutorials outline where to download and how to install the PubSub+ Software.
-
The messaging connectivity information are the following:
-
Host: <public_ip> (IP address assigned to the VMR in tutorial instructions)
-
Message VPN: default
-
Client Username: sampleUser (can be any value)
-
Client Password: samplePassword (can be any value)
Note: By default, the PubSub+ Software "default" message VPN has authentication disabled.
-
Option 3: Get access to a PubSub+ Appliance
-
Contact your PubSub+ appliance administrators and obtain the following:
- A PubSub+ Message-VPN where you can produce and consume direct and persistent messages
- The host name or IP address of the Solace appliance hosting your Message-VPN
- A username and password to access the Solace appliance
Obtaining Apache Qpid JMS
This tutorial assumes you have downloaded and successfully installed the Apache Qpid JMS client. If your environment differs from the example, then adjust the build instructions appropriately.
The easiest way to install it is through Gradle or Maven.
Get the API: Using Gradle
dependencies {
compile("org.apache.qpid:qpid-jms-client:1.6.0")
}Get the API: Using Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.qpid</groupId>
<artifactId>qpid-jms-client</artifactId>
<version>1.6.0</version>
</dependency>Java Messaging Service (JMS) Introduction
JMS is a standard API for sending and receiving messages. As such, in addition to information provided on the Solace developer portal, you may also look at some external sources for more details about JMS. The following are good places to start
- https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/jms/package-summary.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JavaMessageService
- https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/tutorial/partmessaging.htm#GFIRP3
The last (Oracle docs) link points you to the JEE official tutorials which provide a good introduction to JMS.
This tutorial focuses on using JMS 2.0 (May 21, 2013), for JMS 1.1 (April 12, 2002) see Solace Getting Started AMQP JMS 1.1 Tutorials.
Connecting to the Solace Messaging
In order to send or receive messages, an application must start a JMS connection and a session.
There are three parameters for establishing the JMS connection: the Solace messaging host name with the AMQP service port number, the client username and the optional password.
TopicPublisher.java/TopicSubscriber.java
String solaceHost = args[0];
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new JmsConnectionFactory(solaceUsername, solacePassword, solaceHost);Notice how Apache Qpid JMS 2.0 API combines Connection and Session objects into the JMSContext object.
TopicPublisher.java/TopicSubscriber.java
JMSContext context = connectionFactory.createContext()The session created by the JMSContext object by default is non-transacted and uses the acknowledge mode that automatically acknowledges a client's receipt of a message.
At this point the application is connected to Solace messaging and ready to publish messages.
Publishing messages
A JMS Producer needs to be created in order to publish a message to a topic.
The JMS 2.0 API allows the use of method chaining to create the producer, set the delivery mode and publish the message. We assign its delivery mode to non-persistent for better performance.
TopicPublisher.java
final String TOPIC_NAME = "T/GettingStarted/pubsub";
Topic topic = context.createTopic(TOPIC_NAME);
TextMessage message = context.createTextMessage("Hello world!");
context.createProducer().setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.NON_PERSISTENT).send(topic, message);If you execute the TopicPublisher.java program, it will successfully publish a message, but another application is required to receive the message.
Receiving messages
To receive a message from a topic a JMS Consumer needs to be created.
The JMS 2.0 API allows the use of method chaining to create the consumer, and receive messages published to the subscribed topic.
TopicSubscriber.java
final String TOPIC_NAME = "T/GettingStarted/pubsub";
Topic topic = context.createTopic(TOPIC_NAME);
String message = context.createConsumer(topic).receiveBody(String.class);If you execute the TopicSubscriber.java program, it will block at the receiveBody(String.class) call until a message is received. Now, if you execute the TopicPublisher.java that publishes a message, the TopicSubscriber.java program will resume and print out the received message.
Summarizing
Combining the example source code shown above results in the following source code files:
Getting the Source
Clone the GitHub repository containing the Solace samples.
git clone https://github.com/SolaceSamples/solace-samples-amqp-qpid-jms2
cd solace-samples-amqp-qpid-jms2Building
You can build and run both example files directly from Eclipse or with Gradle.
./gradlew assembleThe examples can be run as:
cd build/staged/bin
./topicSubscriber amqp://<HOST:AMQP_PORT> <USERNAME> <PASSWORD>
./topicPublisher amqp://<HOST:AMQP_PORT> <USERNAME> <PASSWORD>Sample Output
First, start TopicSubscriber so that it is up and waiting for published messages. You can start multiple instances of this application, and all of them will receive published messages.
$ topicSubscriber amqp://<HOST:AMQP_PORT> <USERNAME> <PASSWORD>
TopicSubscriber is connecting to Solace router amqp://<HOST:AMQP_PORT>...
Connected to the Solace router with client username 'clientUsername'.
Awaiting message...Then you can start TopicPublisher to publish a message.
$ topicPublisher amqp://<HOST:AMQP_PORT> <USERNAME> <PASSWORD>
TopicPublisher is connecting to Solace router amqp://<HOST:AMQP_PORT>…
Sending message 'Hello world!' to topic 'T/GettingStarted/pubsub'...
Sent successfully. Exiting...Notice how the published message is received by the TopicSubscriber.
Awaiting message...
Message received: 'Hello world!'You now know how to use Apache Qpid JMS 2.0 API over AMQP using Solace messaging to implement the publish/subscribe message exchange pattern.